Happy New Year, everybody!
Time really flew since I returned from my semester abroad, and I admit that I’m feeling a bit Rome-sick! Maybe it’s the chilly Boston weather and lack of Italian on the streets that make me miss the Eternal City.
Besides unpacking (and taking a lot of naps because of my jetlag), I spent my winter break re-acquainting myself with my home city. I went to see a special exhibition at the Museum of Fine Arts, a place I’ve loved since I was a child. I’m glad I made it to the museum before the exhibition closes on the 20th – it was a wonderful experience!
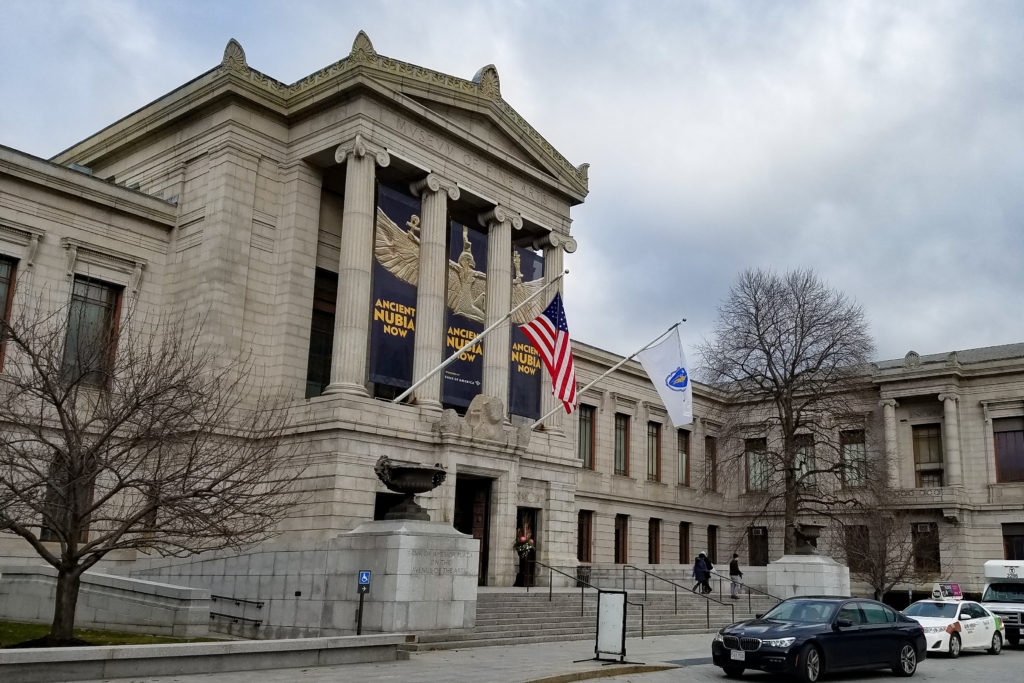

The exhibition was called “Ancient Nubia Now” and features artifacts uncovered during joint excavations between the Museum of Fine Arts and Harvard University in the 1910s and ’20s. Ancient Nubia was a civilization in Africa that covered what is now south Egypt and most of Sudan.
According to the information in the exhibit, several scholars have overlooked or even completely dismissed the artifacts, focusing instead on ancient Egypt. Several panels in the exhibit address the historical biases against the civilization and state how the museum strives to move ancient Nubia into the spotlight it was denied decades before.
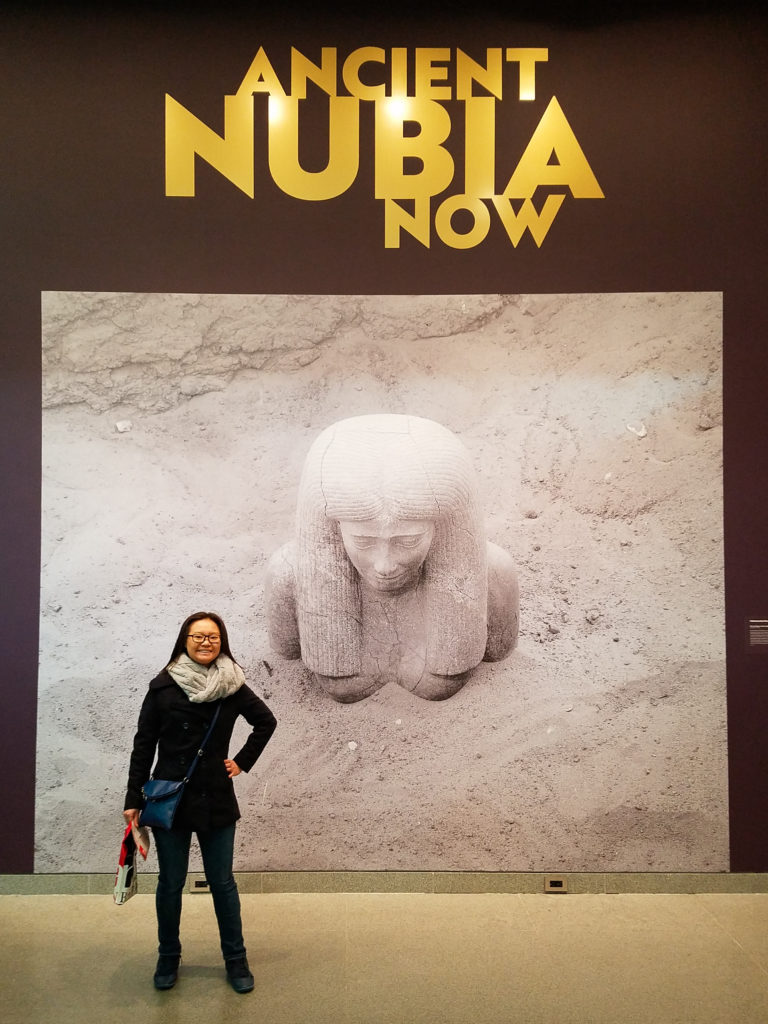

I was blown away by the first room of the exhibit – so many objects that, despite being created millenia ago, are so well-preserved that they look like they were made recently! I loved the turquoise-blue pigments on the stone.
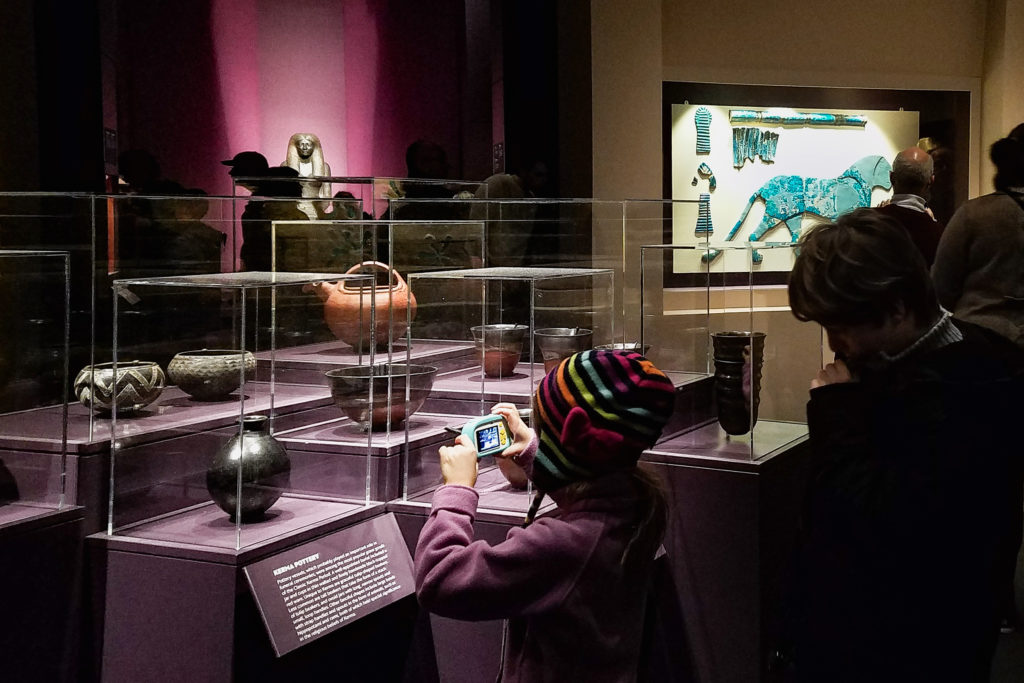
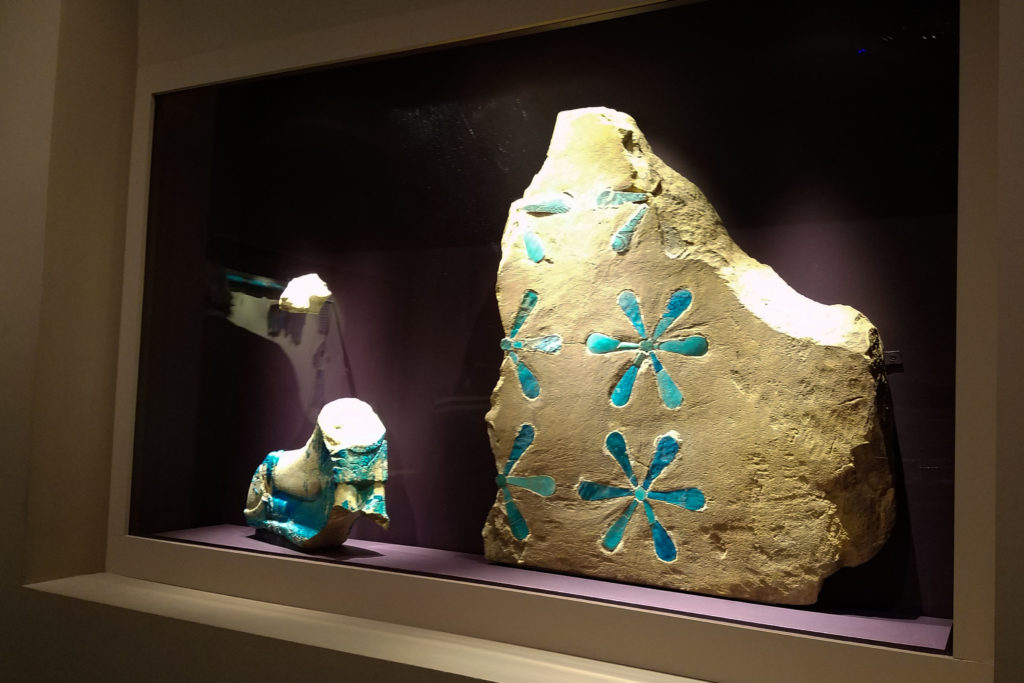


The main site of the early-20th century excavations in Sudan was Kerma, an ancient Nubian city founded in 2400 B.C.E. It was the center of the civilization for centuries and holds a plethora of artifacts and cultural remnants still being studied today.
The ancient Nubians rivaled the ancient Egyptians and fought with them in the mid-16th century B.C.E., after which the Egyptians conquered Kerma. Since then, the ancient Nubians were incorporated into ancient Egypt and adopted cultural influences from their neighbors to the north. The center of Nubian civilization was no longer at Kerma and was instead situated in a city called Meroe after Egypt occupied Nubia until the first millenium B.C.E.
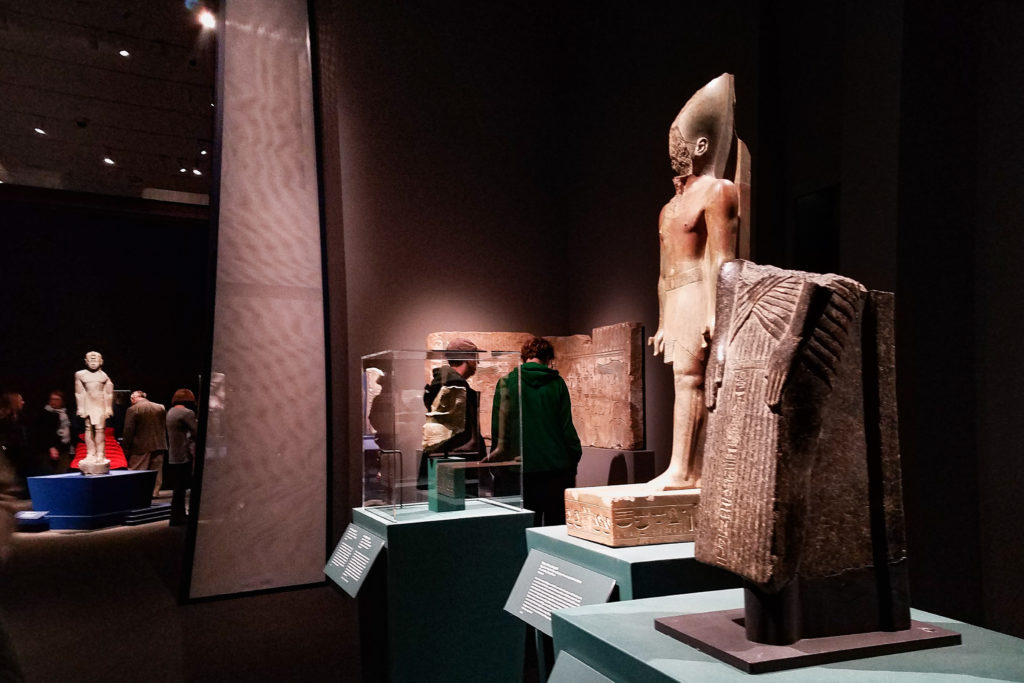
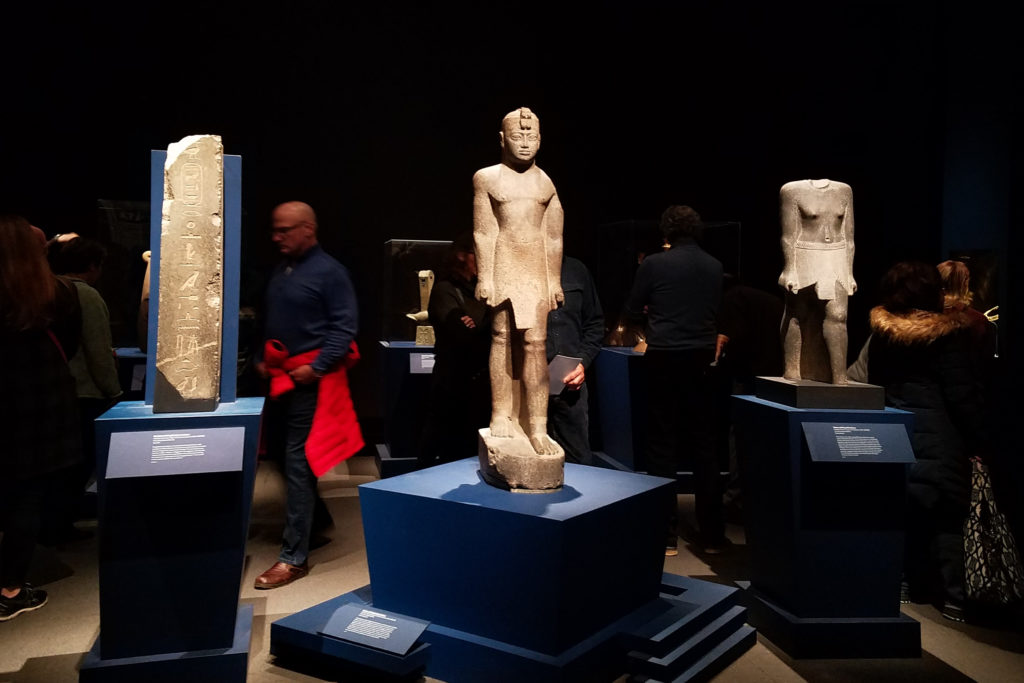
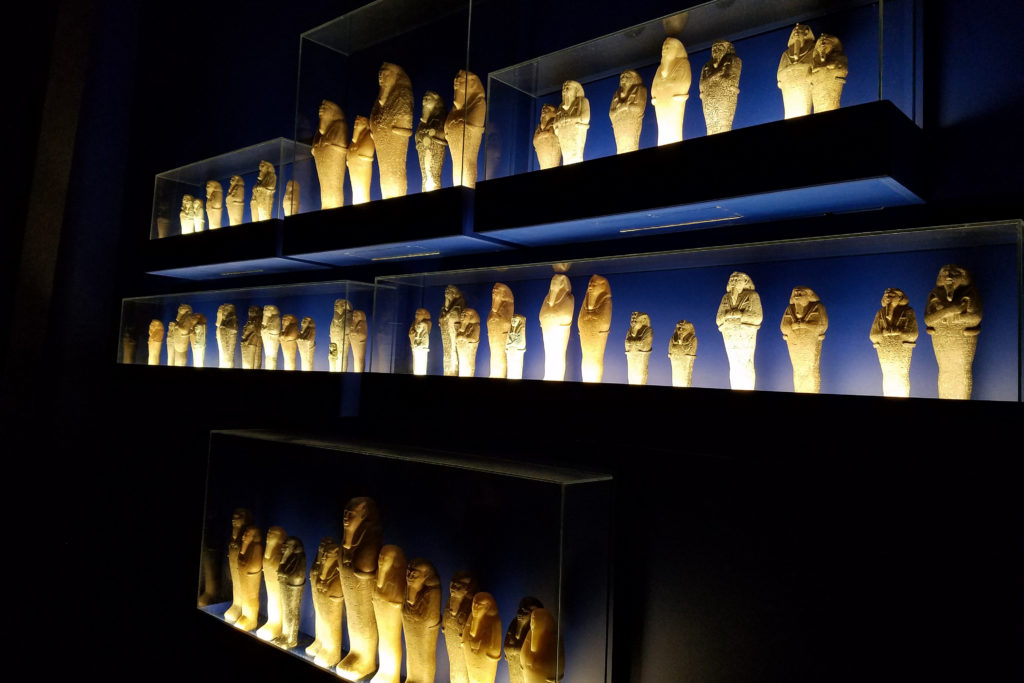



Further in the exhibit, I read about how this assimilation may have contributed to negative opinions of the ancient Nubians in the past. The scholars who dismissed the findings at Kerma were more focused on ancient Egypt, the civilization which they saw as the more powerful body in Africa. Some did not even consider the ancient Nubians as a separate people from the ancient Egyptians because of the cultural incorporation. Furthermore, the Nubians were seen as enemies of the ancient Egyptians and were portrayed negatively in their records.
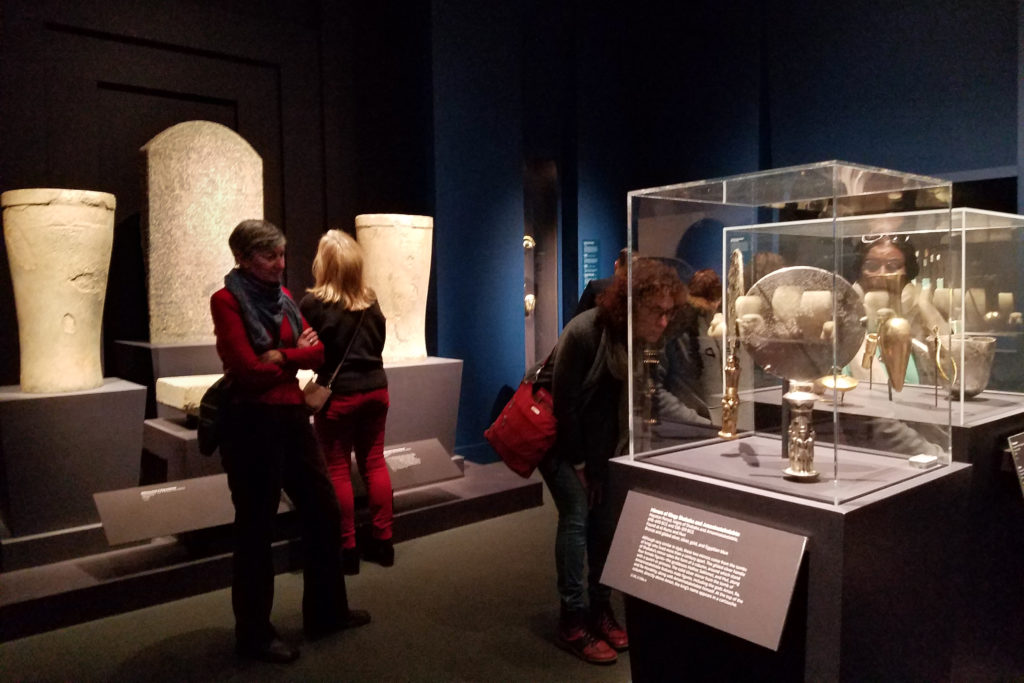

The Museum of Fine Arts seeks to rectify these past biases. There were videos of archaeologists speaking about present work on ancient Nubia and of people who were moved by this new perspective of an ancient civilization. There were photographs and excerpts telling the story of the excavations as well. I found these helpful in keeping these artifacts in the context of the interpretations of the findings.
One of the last things I saw in the exhibit made me smile. It was a display about the influence of Greco-Roman art on ancient Nubia. It was fascinating to see artifacts that looked similar to the things I saw while I was in Rome.
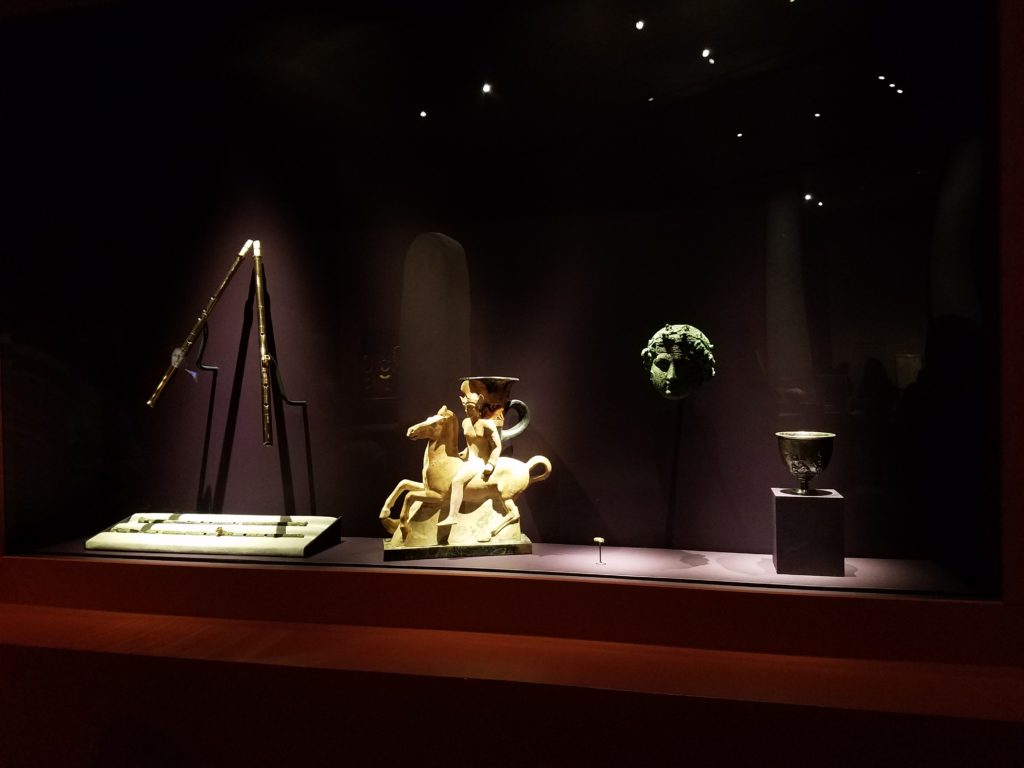

My experience in “Ancient Nubia Now” made appreciate the education I got in Rome last semester even more. In particular, I am grateful for the opportunities I had to explore so much of the ancient world in my Race in the Ancient Mediterranean class.
The exhibit in Boston reminded me of the exhibits on other ancient peoples I saw in Rome. From my off-campus lessons, I learned to examine narratives from different perspectives. The information on the ancient Nubians reminded me of what I learned about the ancient Etruscans at the Museo Nazionale Etrusco di Villa Giulia in September.
The ancient Etruscans formed a civilization in the Italian peninsula before ancient Romans did. They were eventually incorporated into ancient Rome, which became the civilization that is more commonly studied today. The ancient Nubians created an early civilization that was incorporated into ancient Egypt, which was seen as the major power in the academic spotlight. Both the Etruscans and the Nubians were overshadowed by the ancient Romans and ancient Egyptians, respectively.
The exhibit also reminded me of the temporary “Carthago” exhibit at the Colosseum. I think the ancient Nubians are similar to the ancient Carthaginians in that they were perceived as the “enemy” in another power’s eyes. Kerma was destroyed after the ancient Egyptians conquered Nubia, and Carthage was destroyed after the Romans won the Third Punic War. Both “Ancient Nubia Now” and “Carthago” display the remnants of the two obscured cultures from a lesser-known perspective.
Had I not gone to Rome, and had I not taken Race in the Ancient Mediterranean, I would not have been able to enjoy learning about ancient Nubia to this degree. I’ve gained not only more knowledge from a different point of view, but also more advanced critical thinking skills. I’m proud of how much I got out of my museum visit back home. I know someone who will be amused by adventures here as well.